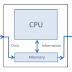
.jpg) one of the major advantages that digital system have over analog systems is the ability to esily store large quantities of digital information and data for short of long periods of time. this memory capability is what makes digital computer so versatile and adaptable to many situations. for example, in a digital computer the internal main memory stores instruction that tell the computer what to do under all possible circumstances so that the computer will do its job with a minimum amount of human intervention, magnetic type and magnetic disk are popular mass storage devices that are much less expensive in cost per bit that internal memory devices.
one of the major advantages that digital system have over analog systems is the ability to esily store large quantities of digital information and data for short of long periods of time. this memory capability is what makes digital computer so versatile and adaptable to many situations. for example, in a digital computer the internal main memory stores instruction that tell the computer what to do under all possible circumstances so that the computer will do its job with a minimum amount of human intervention, magnetic type and magnetic disk are popular mass storage devices that are much less expensive in cost per bit that internal memory devices. MEMORY TERMINOLOGY
MEMORY TERMINOLOGYMEMORY CELL
this is device or electrical circuit used to store a single bit (0 or 1).
MEMORY WORD
this is group of bits (cells) in a memory that represents information of data of some type. word size in modern computers typically ranges from 4 to 64 bits,depending on the size of the computer.
 BYTE
BYTEthis is special term used for a 8-bit word. in modern digital computers, the word size is usually a multiple of 8-bits such as 2 bytes or 4 bytes.
MEMORY CAPACITY
this is way of specifying how many bits can be stored in a particular memory device of computer memory system.to illustrate, suppose that we have a memory devices,which can store 4096 20-bits words. its represent a total capacity of 81,920 bits. we could also express its memory's capacity as 4096 x 20. when expressed with way, the first number (4096) is the number of words and the secant number (20) is the number of bits par word (word size). computer memory is measured in terms
of bytes. the large units are kilobyte, megabyte and gigabyte.
RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY (RAM)
tis refers to memories in which the actual physical location of memory word has no effect on how long it takes to read or write into that location. in other words, the accsess time is the same for any address in memory. most semiconductor memries and magnetic disk memories are random access memories
 22:10
22:10





.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

No comments
Post a Comment